During long-flight, what should be aware?
(International Patient Assistance Center) article author : Jirawat Tawaro, M.D.
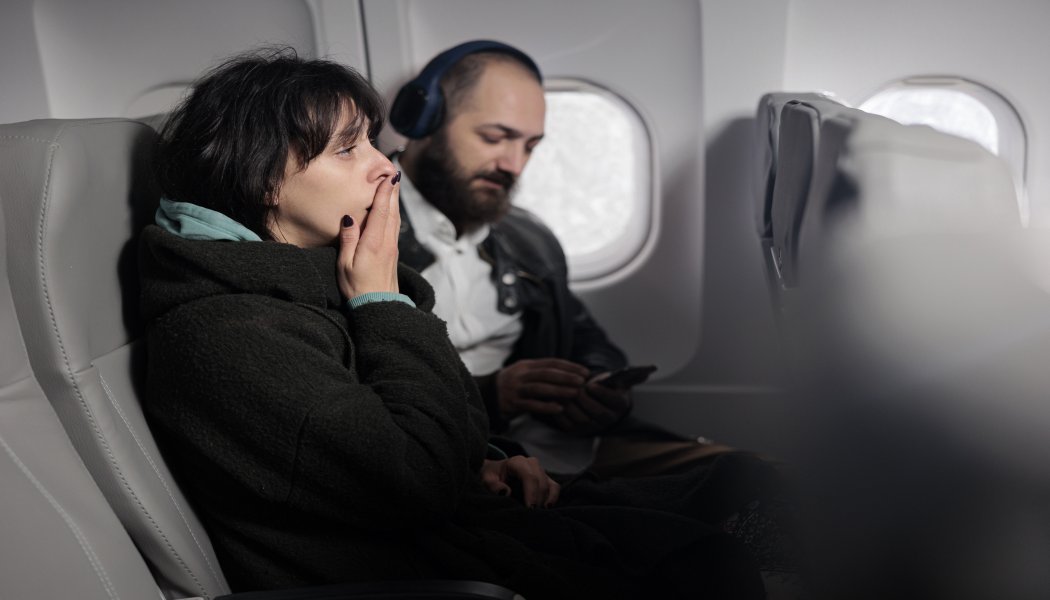

Traveling by plane for long periods of time can pose health risks for people with certain medical conditions. The air pressure and humidity in the cabin are lower than at ground level, which can lead to a number of problems, including:
1. Hypoxia: Reduced oxygen levels in the blood, which can worsen the symptoms of certain conditions, such as heart disease, asthma, and COPD.
2. Changes in barometric pressure: As the plane ascends and descends, gas trapped in the body expands and contracts, which can cause pain, discomfort, and even medical emergencies.
3. Low humidity: Dry air can cause skin, eye, and mouth irritation.
4. Reduced mobility: Sitting for long periods can lead to blood clots, swelling, and other health problems.
5. Motion sickness: Some people are more prone to motion sickness than others.
6. Jet lag: The body's natural clock can be thrown off by traveling across time zones, leading to fatigue, difficulty sleeping, and other symptoms.
People with the following medical conditions should consult with the doctor before traveling by plane:
- Heart disease
- Coronary artery bypass graft
- Hypertension
- Venous thrombosis
- Asthma
- COPD
- Pneumothorax
- Infectious disease
- Cerebrovascular disease
- Epilepsy
- Anemia
- Diabetes
- Psychiatric disorders
- Recent surgery
- Pregnant women and infants should also take precautions before flying.
To reduce the risk of health problems while traveling by plane, passengers should:
- Get enough rest before the flight and try to nap during the flight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Choose flights that are as short as possible.
- Choose flights that depart and arrive at times that are close to your body's natural clock.
- Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
- Move around and stretch every few hours.
- Wear comfortable clothing and shoes.
- Bring any medications you need.
- By following these tips, you can help ensure a safe and comfortable flight.
Location : 1st Floor, Building B
Service hours : 08.00-20.00
Contact : 033-038853
ID Line : @schinter
Email : [email protected]